Locking Mechanism¶
In any multi-user application a locking mechanism is necessary to avoid conflicts when the same table is updated by two people or processes. In Data Controller this is handled using the DCLIB.MPE_LOCKANYTABLE table, specifically using the mp_lockanytable macro.
This macro is invoked whenever a process requires an exclusive lock on a table - first to mark the table as locked, and again to mark it as unlocked. The logic flow is demonstrated below:
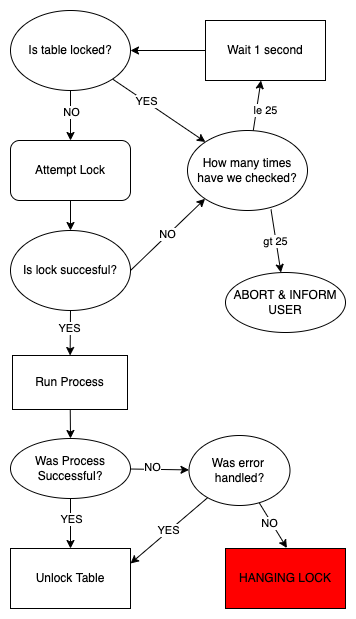
Notice above the red box - this situation can occur in unusual circumstances (such as a system shutdown or OS error). If you are waiting more than a minute or two for a table to be unlocked, then it is advised to follow the process below.
Unlock Process¶
Before proceeding with an unlock, the first step should be to understand why the process is locked. By opening the MPE_LOCKANYTABLE table it will be possible to see which user performed the lock, and when. Simply filter the table where LOCK_STATUS_CD='LOCKED'.
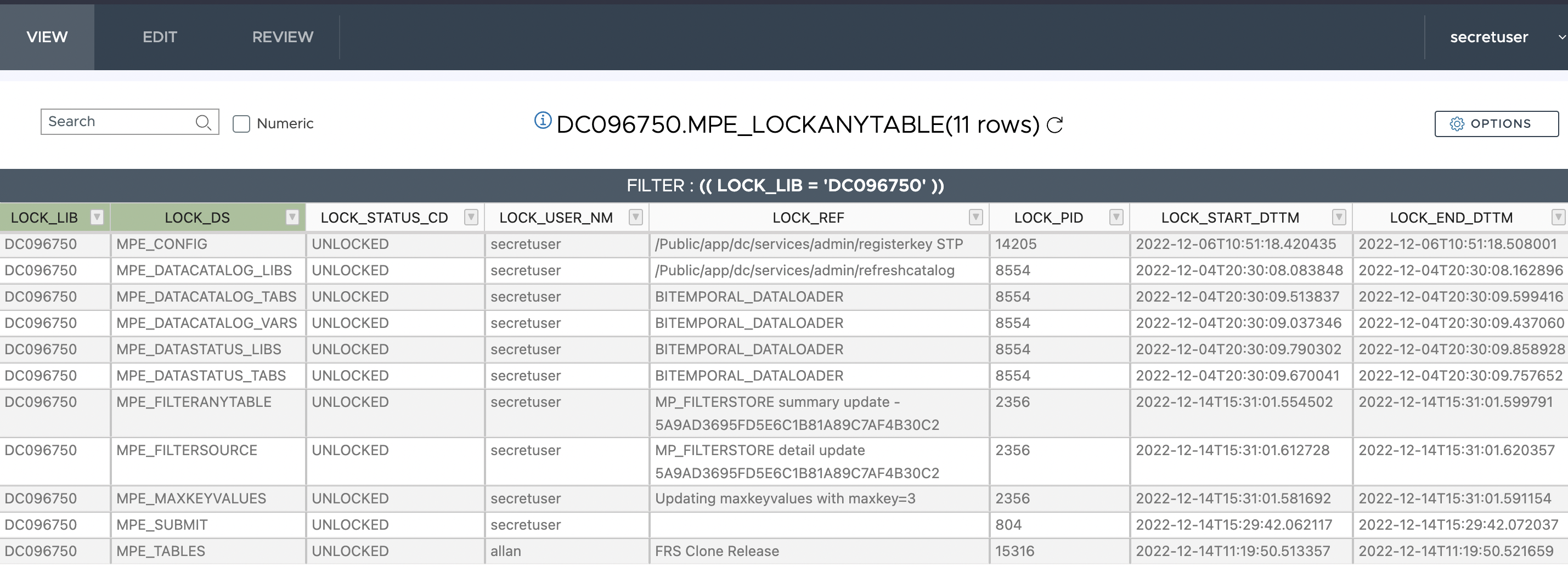
If an unlock is deemed necessary, simply open this table in the EDIT menu, and change the value of LOCK_STATUS_CD from LOCKED to UNLOCKED.
Scalability¶
This locking mechanism does not scale well if the table remains in SAS dataset (.sas7bdat) form. If you are deploying Data Controller for usage beyond 10-20 users then you are advised to put the control tables (DC library) in a database.
Third Party Applications¶
Third party SAS apps may also make use of this locking table. This is handled by simply:
- Ensuring the DC library is assigned in the Service
- Using the mp_lockanytable macro to perform the lock
- Using the mp_lockanytable macro to perform the unlock
- Performing appropriate error handling to ensure an unlock if there are any issues in the service